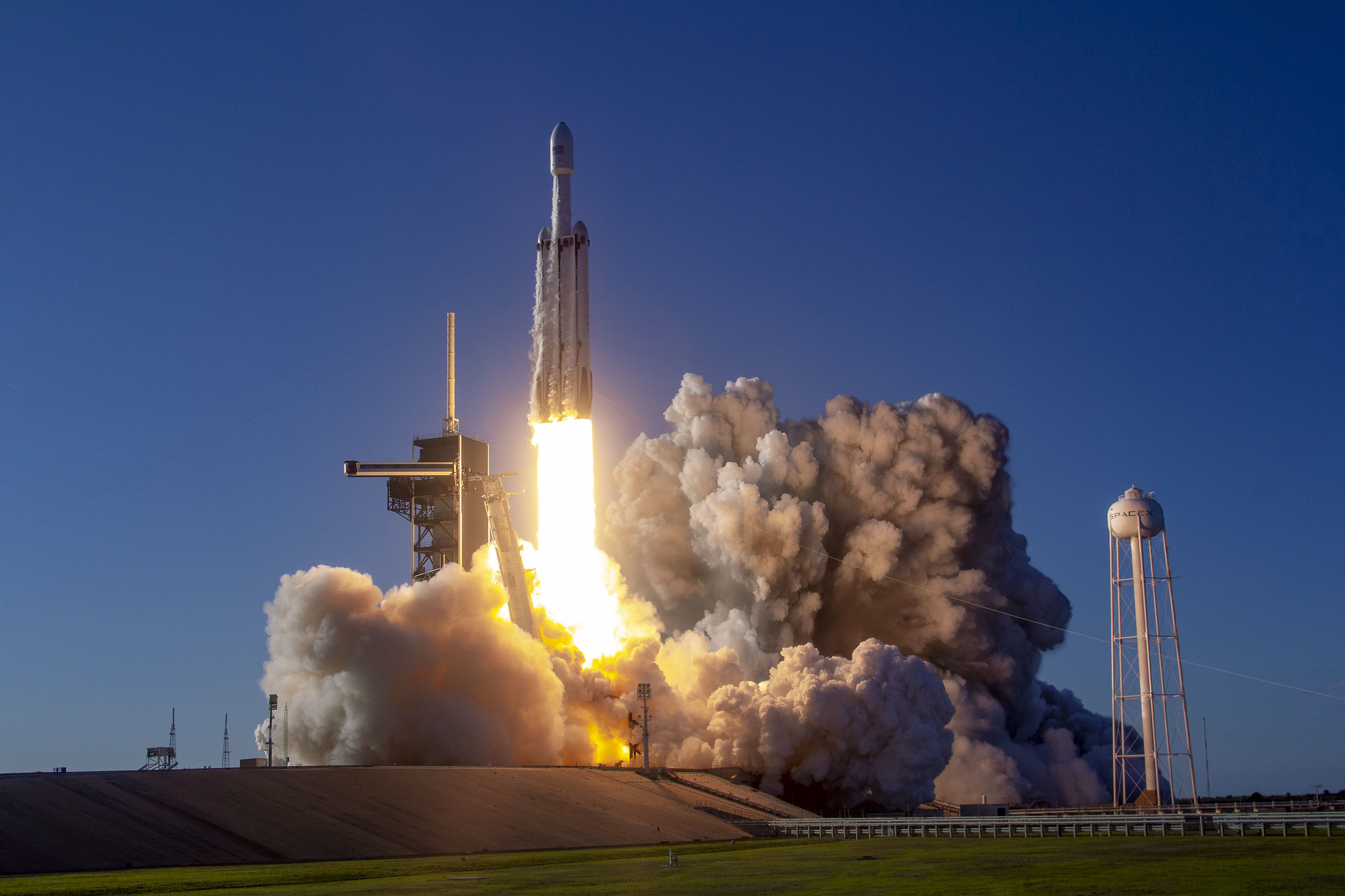
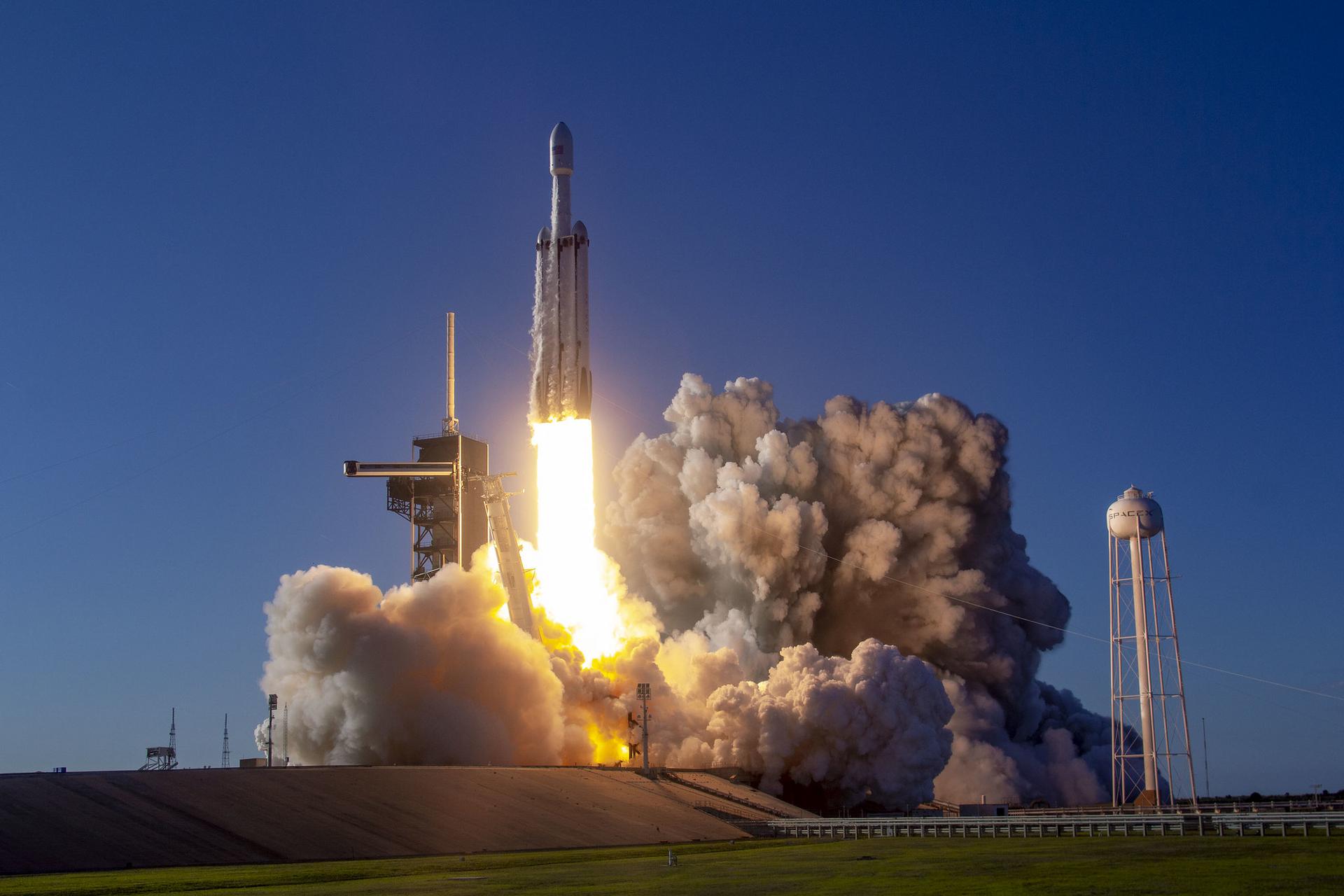
Astrobotic has signed a launch contract with SpaceX. Its goal is to deliver the descent platform Griffin with the VIPER (Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover) rover to the Moon. The Falcon Heavy rocket was chosen for this mission.

VIPER must land in one of the southern subpolar craters, the bottom of which is constantly in shadow. The main task of the apparatus is to study the lunar soil in order to determine the percentage of water ice in it. For this purpose, the moon rover will be equipped with a drill, which allows to extract samples from a depth of one meter, and three scientific instruments. Neutron detector NSS will help to identify locations of the likely occurrence of ice, spectrometers MSolo and NIRVSS – to determine the chemical composition of regolith. The duration of the mobile laboratory should be at least 100 days.
While the rover itself is being created by NASA engineers, the task of delivering it to the moon was assigned to the company Astrobotic, which received from the U.S. Aerospace Administration contract worth $ 199.5 million. She took on the construction of the descent vehicle and the search for the launch operator. The Griffin platform, involved in the mission, is a more powerful version of the Peregrine spacecraft. It is planned to send it to the Moon this year, using a new rocket Vulcan, created by the alliance ULA. As for the rover VIPER, it will be launched in 2023.
Astrobotic did not say why it decided to change the launch operator for its second lunar mission. The amount of the contract with SpaceX is also not disclosed. At the site of the company itself, the Falcon Heavy launch is now estimated at $90 million.
It is also worth noting that since the start of design of the VIPER rover in 2019, its cost has increased markedly. Initially it was estimated at $250 million, but at the moment it is already $433 million.