Interesting News – Incredible stories, Ufo, History, Animals, Photos & Videos
Strange news
Planet Earth
Woman was declared dead for over ten minutes and encountered celestial beings…
A physician was incensed after a group of ramblers parked three sizeable…
Professor Xueqin Jiang gained notoriety for his accurate forecasts concerning Trump’s 2024…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
HISTORY
The Cold War vestige has been interred since 1968. Share Article Share…
EXCLUSIVE: Vile fiend had asserted partner’s granddaughter had not returned from a…
Researchers in Germany posit that markings and etchings on Stone Age relics…
HEALTH
COVID-19 Shot in Pregnancy Could Lower Preeclampsia Odds
A hypertensive ailment, preeclampsia, can jeopardize the wellness of both…
Excess Weight Could Raise Risk of Death from Serious Infections,…
“`html Excess weight is correlated with an elevated susceptibility to…
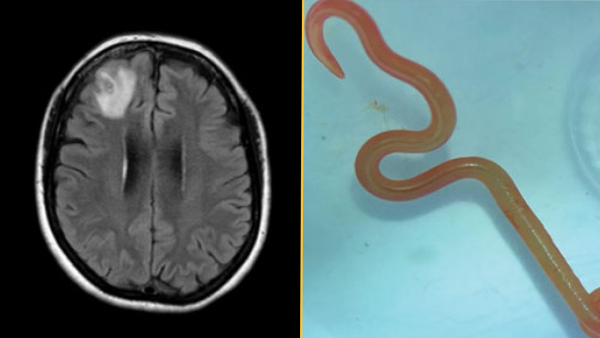
Medical Mystery: Novel Parasite Causes Lung Ailment, Organ Failure, and…
It turns out that a vivid, parasitic worm was the…
ANIMALS
Nature’s Summons: Will Humanity Respond? Why nurturing our interspecies bonds…
MEMBER EXCLUSIVE Communities in Mozambique partner with honeyguide birds to…
Genetic Toggle Transforms Nurturing Mouse Fathers into Aggressive Ones, Say…
An African striped mouse sire cuddles with some of his…
Spinosaurus: Ancient Sahara Wader with a Curved Head Crest, Dubbed…
“`html The image presents Spinosaurus mirabilis positioned by a riverbank…
SPACE AND UFO
Biggest-ever charting of the Galaxy’s heart exposes ‘scarce and mysterious’…
The Milky Way’s Central Molecular Zone (CMZ) encompasses the supermassive…
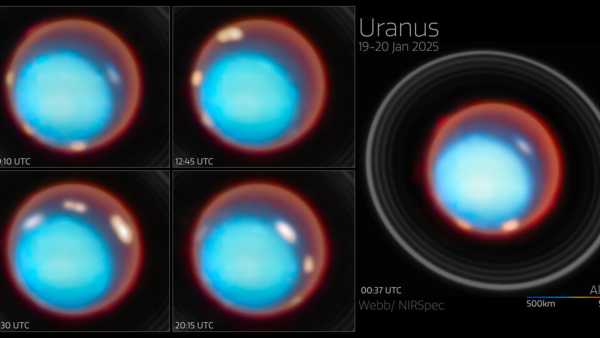
‘One of the strangest in the solar system’: James Webb…
“`html JWST took notice of Uranus as it revolved for…
Crimson Moon 2026: Viewing the Complete Lunar Eclipse Live Online…
“`html The full eclipse of the moon on March 3,…