
Three factors cause the symptoms of an asthma attack. (Image credit: pocketlight via Getty Images)
An asthma attack is a sudden worsening of asthma symptoms that occurs due to inflammation and narrowing of the airways. This can make breathing difficult and, in severe cases, be life-threatening.
Hundreds of millions of people worldwide suffer from asthma, and attacks can be triggered by allergens, respiratory infections, cold air, exercise, or irritants like smoke and pollution. But what actually happens in the body during an asthma attack?
“There are two major physiological changes that occur during an asthma attack,” says Allen Dosor, MD, professor of pediatrics and chief of the division of pulmonary, allergy, and sleep medicine at New York Medical College.
The first is bronchospasm, Dozor told Live Science. During an asthma attack, the bronchi of the lungs — the tubes that connect the trachea to the lungs — spasm and narrow, making it difficult to breathe.
The second change, he said, is airway inflammation, the body’s response to inhaled allergens or pollutants. “Inflammation is quite a complex process, but we now understand that some asthmatics have minimal inflammation, while others have significant inflammation,” Dozor said.
In addition to bronchospasm and inflammation, mucus production may also play a role in the development of asthma. The lungs produce thick mucus that blocks narrowed airways and makes breathing difficult. People with asthma often experience ongoing inflammation of the airways, which leads to chronically elevated levels of mucus production, as well as thickening of the airway lining over time. Furthermore, during an asthma attack, there is a short-term surge in mucus production caused by inflammatory chemicals and molecules such as histamine and leukotrienes produced by immune cells.
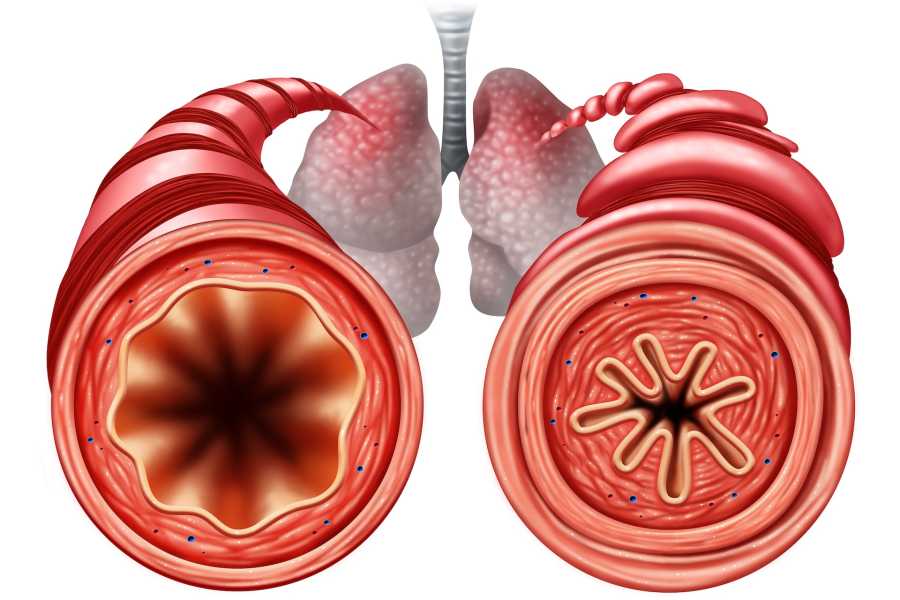
During an asthma attack, the airways become inflamed, narrow, and filled with mucus, making it difficult to breathe.
These three factors—bronchospasm, inflammation, and mucus—work together to create breathing difficulties, leading to the characteristic symptoms of an asthma attack, including wheezing, shortness of breath, coughing, and a feeling of chest tightness.
When the airways begin to close, it becomes difficult for the body to get enough oxygen. In mild cases, this can lead to shortness of breath and coughing, but in more severe attacks, oxygen levels can drop significantly, causing dizziness, confusion, and even loss of consciousness. Without proper treatment, a severe asthma attack can be fatal.
The most effective way to treat an asthma attack
Sourse: www.livescience.com





