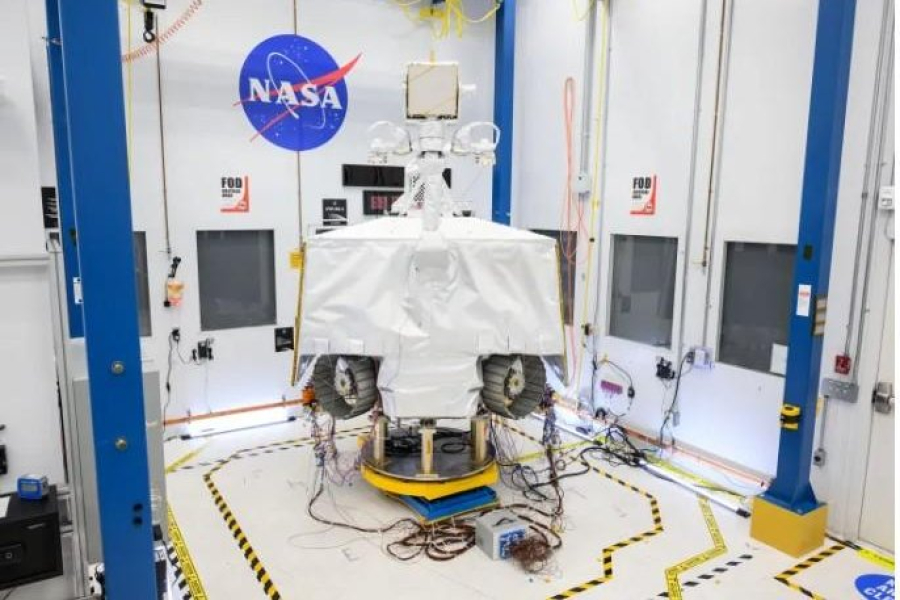
NASA is exploring new ways to get its VIPER rover to the moon after canceling proposals to collaborate on landing a water-seeking robot on the lunar surface.
VIPER (short for Volatiles Investigating Polar Explorer Rover) is designed to explore the harsh conditions of the Moon's south pole in search of ice and other potential resources.
NASA said Wednesday it has canceled new partnership proposals to send VIPER to the lunar surface without government spending. NASA is set to announce a new strategy.
On July 17, NASA suspended the lunar rover project developed jointly with Lockheed Martin and General Motors.
A NASA analysis found that previous cost increases, launch delays, and potential for further cost increases made the project uneconomic. The rover was originally scheduled to launch in late 2023, but was delayed to give more time to the Astrobotic lander.
NASA said it would disassemble and reuse VIPER tools and components for future lunar missions.
NASA issued a Request for Information on August 9 to solicit interest from U.S. companies and institutions in conducting a mission using the VIPER rover. Applications were due by March 5, with results expected to be announced this summer.
However, those plans were put on hold on Wednesday.
“We are grateful to all who offered to collaborate through the Volatile Science Partnership Announcement on the Moon,” said Nicky Fox, associate administrator for the Science Mission Directorate at NASA in Washington, D.C. “We look forward to continuing volatiles research with VIPER as NASA continues its efforts to explore the Moon and Mars.”
VIPER is designed to explore the moon with three instruments and a 3.28-foot drill to detect and analyze different lunar soil environments at varying depths and temperatures. This includes permanently shadowed craters, which scientists believe are among the coldest places in the solar system, with temperatures as low as minus 334 degrees Fahrenheit.
Lunar resource maps will be used in NASA's Artemis manned missions, including resource collection to support a long-term presence on the lunar surface.
Griffin's goal was to land VIPER on the Moon.
Astrobotic has a backup rover that could be sent on a SpaceX Starship mission with two astronauts on the lunar module. FLIP, which stands for Flex Lunar Innovation Platform, is a robotic four-wheel vehicle that weighs about 1,000 pounds and can carry up to 66 pounds of payload.
The agency is planning a 10-day crewed mission around the moon in April 2026 with four astronauts, the first time since Apollo 17 landed humans on the lunar surface in 1972.
The first human landing on the Moon as part of the Artemis III program is planned for mid-2027.
While NASA partners with SpaceX on missions including the International Space Center, the Space Launch System rocket is built by Boeing and Northrop Grumman, and the Orion spacecraft is built by Lockheed Martin. SpaceX is involved in developing two landers on the moon: the Lunar Surface Access Program and the Lunar Gateway, a space station in lunar orbit.
In 2022, the Artemis I spacecraft entered lunar orbit with a dummy.
Sourse: www.upi.com