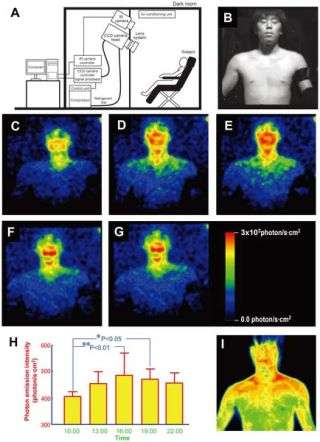
Schematic illustration of experimental setup that found the human body, especially the face, emits visible light in small quantities that vary during the day. B is one fo the test subjects. The other images show the weak emissions of visible light during totally dark conditions. The chart corresponds to the images and shows how the emissions varied during the day. The last image (I) is an infrared image of the subject showing heat emissions.
The human body literally glows, emitting a visible light in extremely small quantities at levels that rise and fall with the day, scientists now reveal.
Past research has shown that the body emits visible light, 1,000 times less intense than the levels to which our naked eyes are sensitive. In fact, virtually all living creatures emit very weak light, which is thought to be a byproduct of biochemical reactions involving free radicals.
(This visible light differs from the infrared radiation — an invisible form of light — that comes from body heat.)
To learn more about this faint visible light, scientists in Japan employed extraordinarily sensitive cameras capable of detecting single photons. Five healthy male volunteers in their 20s were placed bare-chested in front of the cameras in complete darkness in light-tight rooms for 20 minutes every three hours from 10 a.m. to 10 p.m. for three days.
The researchers found the body glow rose and fell over the day, with its lowest point at 10 a.m. and its peak at 4 p.m., dropping gradually after that. These findings suggest there is light emission linked to our body clocks, most likely due to how our metabolic rhythms fluctuate over the course of the day.
Faces glowed more than the rest of the body. This might be because faces are more tanned than the rest of the body, since they get more exposure to sunlight — the pigment behind skin color, melanin, has fluorescent components that could enhance the body’s miniscule light production.
Since this faint light is linked with the body’s metabolism, this finding suggests cameras that can spot the weak emissions could help spot medical conditions, said researcher Hitoshi Okamura, a circadian biologist at Kyoto University in Japan.
“If you can see the glimmer from the body’s surface, you could see the whole body condition,” said researcher Masaki Kobayashi, a biomedical photonics specialist at the Tohoku Institute of Technology in Sendai, Japan.
The scientists detailed their findings online July 16 in the journal PLoS ONE.
Sourse: www.livescience.com





