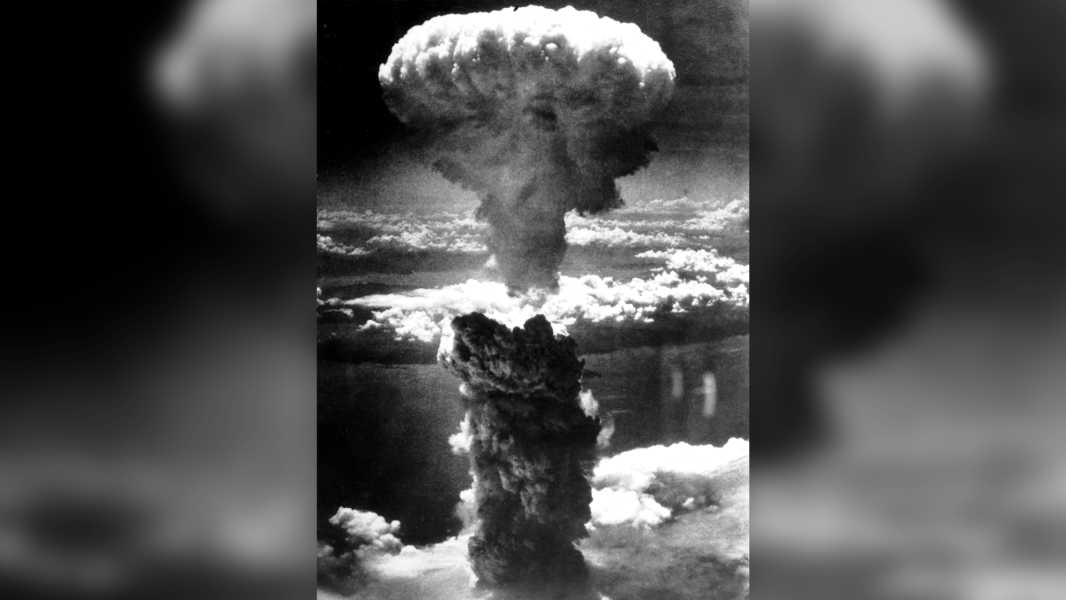
Pictured is the mushroom cloud that formed after a nuclear bomb exploded over Nagasaki, Japan, on August 8, 1945. (Image credit: Photo12/Universal Images Group via Getty Images)
Christopher Nolan's Oppenheimer, released amid the ongoing conflict between Russia and Ukraine, has refocused public attention on nuclear weapons at a time when the threat of a nuclear conflict is growing.
But what would a nuclear bomb explosion look like to people on earth, and what would happen after that?
The answer, of course, depends on the number of weapons dropped. According to the Federation of American Scientists, Russia and the United States possess 90 percent of the world’s nuclear arsenals. Russia has 1,588 nuclear weapons, deployed on intercontinental missiles with a range of at least 3,417 miles (5,500 kilometers) and on heavy bombers that can carry and drop nuclear warheads, while the United States has 1,644 of the same type. (Both countries also have about 5,000 active bombs ready to launch.) A full-scale nuclear war would be catastrophic for humanity—not only because of the immediate casualties but also because of the global cooling known as a nuclear winter that would follow.
Some foreign policy experts believe a limited nuclear conflict using so-called tactical nuclear weapons is more likely. Between 30% and 40% of the U.S. and Russian arsenals consist of these smaller bombs, which have a range of less than 310 miles (500 kilometers) by land and less than 372 miles (600 kilometers) by sea or air, according to the James Martin Center for Nonproliferation Studies. While these weapons would still cause significant damage near ground zero, they would not lead to the worst-case scenario of a global nuclear apocalypse.
When a nuclear bomb explodes
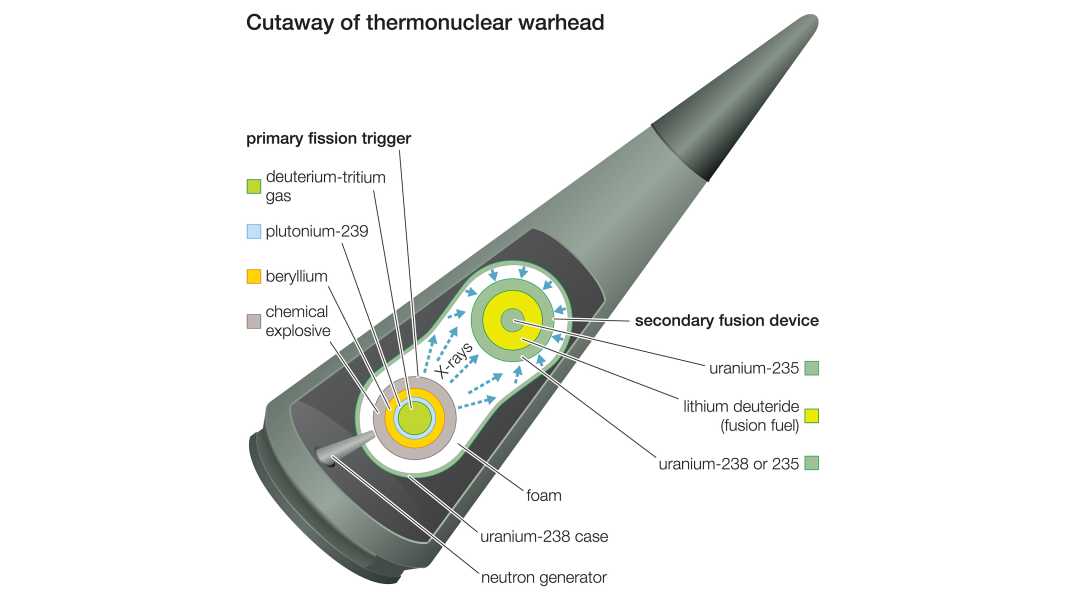
Both fission and fusion reactions are used to create the explosion of a thermonuclear warhead.
There are many types and sizes of nuclear weapons, but modern bombs begin by triggering a fission reaction. Fission is the process of splitting the nuclei of heavy atoms into lighter ones, releasing neutrons. These neutrons can interact with the nuclei of neighboring atoms, causing them to split and starting an uncontrolled chain reaction.
Fission produces a devastating explosion: it was fission bombs, sometimes called atomic bombs, that destroyed Hiroshima and
Sourse: www.livescience.com





