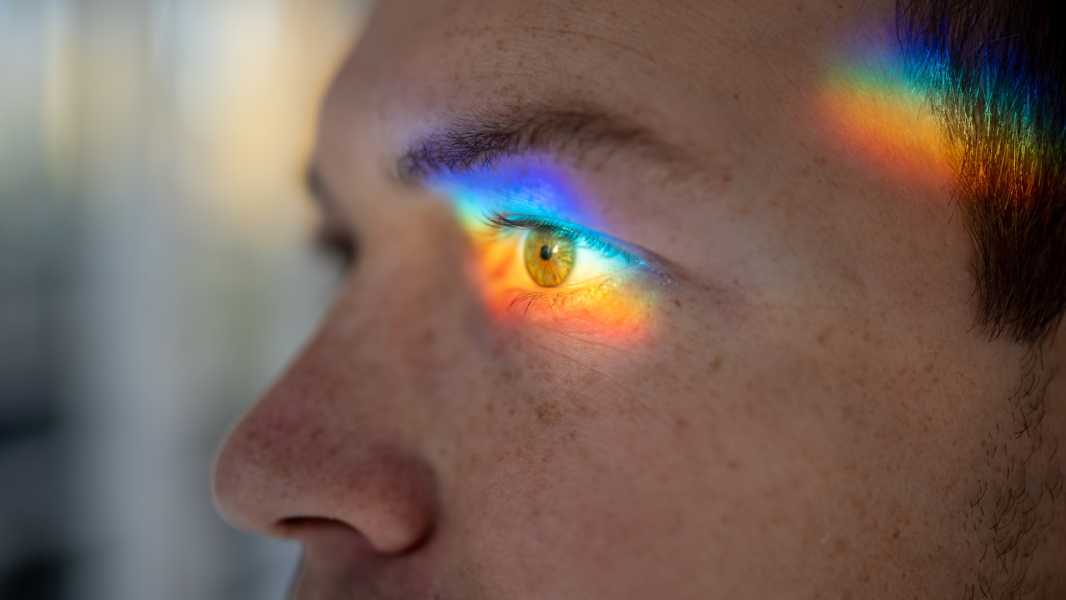
Color blindness is mostly seen in men. It is caused by genetic predisposition. (Photo: Dima Berlin, Getty Images)
An estimated 300 million people worldwide suffer from color blindness. This typically means they can't distinguish between certain shades of color, have trouble judging the brightness of colors, or, in rare cases, can't perceive color at all. However, color blindness affects men and women differently. According to the Cleveland Clinic, about 1 in 12 men and 1 in 200 women have the condition.
So how is it that there are significantly more men who are colorblind than women?
The answer can be found in the genetics of the human eye. Humans distinguish colors thanks to specialized cells located at the back of the eyeball called cones. There are three types of cones, each with a maximum sensitivity to certain wavelengths of light.
You may like
-

Why are men taller than women on average?
-

Scientists have solved the mystery of the origin of red cats and why there are so many males among them.
Sourse: www.livescience.com