“`html

An innovative investigation starts to make associations between unease, sleeplessness, and weakening of the defense system.(Image credit: Maria Korneeva/Getty Images)ShareShare by:
- Copy link
- X
Share this article 1Join the conversationFollow usAdd us as a preferred source on GoogleNewsletterSubscribe to our newsletter
Tension, worry, and restless evenings accomplish beyond disrupting inner calmness — they might additionally impair the body’s safeguard, causing people to be more exposed to diseases, malignant growths, and immune system conditions. At present, researchers have revealed a possible system that might connect these mental components and resistance issues.
Within another exploration, distributed on Dec. 10 in the diary Frontiers in Immunology, specialists centered around a sort of safe cell called natural killer (NK) cells that might assume a significant part.
You may like
-
Heart attacks show less damaging effects during the night, a point that could be key for developing effective treatment strategies.
-

Researchers just characterized five distinct sleep patterns — with some showing potential for identifying mental disorders
-

Research implies the process of getting older and the existence of swelling might not correlate as strongly as once believed
This discovery drove immunologist Renad Alhamawi, the study’s primary creator from Taibah University in Medina, Saudi Arabia, to investigate how uneasiness could impact insusceptibility in ladies.
Alhamawi and her associates enlisted 60 female understudies matured 17 to 23 and requested that they finish a survey about their emotional wellness. The reactions showed that 75% detailed side effects reliable with GAD — like feeling apprehensive, being so eager that it’s difficult to sit still, or getting handily fractious— including 13% with extreme side effects. (Despite the fact that the members were evaluated for GAD side effects, none were authoritatively determined as a component of this review.)
Around 53% of the gathering, or 32 understudies, revealed insufficient sleep.
Next, the scientists gathered blood tests from the members and surveyed the degrees of different resistant cells, which uncovered that the individuals who encountered uneasiness-like side effects had 38% less NK cells than those without side effects.
NK cells are one of the primary sorts of resistant cells to answer an illness or to the presence of disease in the body, and immunologists split them into two subsets. The first subset produces proteins that breakdown and “kill” sick cells. The subsequent subset works by emitting protein signals, called cytokines, that control other resistant cells. A diminished wealth of these double-activity cells could possibly incline people to sickness.
The members who detailed uneasiness side effects had diminished degrees of the two subsets of NK cells, while individuals detailing lacking rest had 40% less of the insusceptible-controlling subset of cells as it were.
Critically, this study tracked down just a connection between these uneasiness side effects, rest, and diminished NK cell levels; the scientists have yet to investigate a causative connection, not to mention explore whether this drop in NK cells could prompt observably higher paces of sickness.
You may like
-
Heart attacks show less damaging effects during the night, a point that could be key for developing effective treatment strategies.
-

Researchers just characterized five distinct sleep patterns — with some showing potential for identifying mental disorders
-

Research implies the process of getting older and the existence of swelling might not correlate as strongly as once believed
It is yet unclear what factors might underlie this alteration in NK cell amount in the blood stream. As an example, it is possible that the cells die or that the body restores them at a more gradual rate.
Likewise, “zeroing in on coursing NK cells [in the blood] doesn’t permit examination of NK cells penetrating the sensory system,” Stefano Garofalo, an immunologist at the Sapienza University of Rome who was not associated with the work, expressed in an email to Live Science. He hypothesized that the drop in NK cells could happen in the event that they relocate from the blood stream into nerve tissue in individuals who have uneasiness or a sleeping disorder. His exploration centers around how NK cells assist with controlling mind capability and shape conduct in mice.
These discoveries line up with those from other exploration, like a review on ongoing tinnitus, where members who revealed higher feelings of anxiety had less cell-killing NK cells. Alhamawi said that the stress hormone cortisol might drive down NK cell populaces since it is known to apply other safe-smothering impacts. For example, cortisol can obstruct antigen-explicit T cells, a sort of safe cell that perceives highlights of explicit dangers, similar to infections.
“Uneasiness builds the degree of cortisol, so we believe it could influence the quantity of NK cells in a roundabout way,” Alhamawi said.
RELATED STORIES
—Only 1 portion of LSD could reduce nervousness for a considerable length of time, preliminary finds
—Deadly familial a sleeping disorder: A hereditary condition where individuals won’t ever rest from now onward, indefinitely
—Sporadic rest might build your gamble of biting the dust from disease and coronary illness
The ongoing exploration has a couple of provisos. “The primary constraint of the review is the tiny member gathering, comprising solely of ladies under 25 years old and having a place with a solitary ethnic foundation,” Garofalo said. Future examinations could decide whether the connection is more generalizable, utilizing a bigger blended orientation populace of people from various backgrounds.
Alhamawi noticed that she might want to play out a drawn-out study, in which specialists track how nervousness, dozing designs, and NK cell levels change over the long haul in a similar gathering of members. That could give a more clear image of the connection between these mental elements and resistance, as well as the frequency of sickness.
“We can check whether there is [an] impact by testing in the event that they foster more irresistible illness or ongoing sickness,” she added.
Disclaimer
This article is for educational purposes as it were and isn’t intended to offer medical counsel.
TOPICSanxiety

Kamal NahasSocial Links NavigationLive Science Contributor
Kamal Nahas is an independent donor situated in Oxford, U.K. His work has showed up in New Scientist, Science and The Scientist, among other sources, and he principally covers research on development, wellbeing, and innovation. He holds a Ph.D. in pathology from the University of Cambridge and a graduate degree in immunology from the University of Oxford. He presently fills in as a microscopist at the Diamond Light Source, the U.K’s. synchrotron. At the point when he’s not composing, you can track down him chasing after fossils on the Jurassic Coast.
Show More Comments
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again, you will then be prompted to enter your display name.
LogoutRead more
Heart attacks show less damaging effects during the night, a point that could be key for developing effective treatment strategies.

Researchers just characterized five distinct sleep patterns — with some showing potential for identifying mental disorders

Research implies the process of getting older and the existence of swelling might not correlate as strongly as once believed

We may finally understand stress-induced hair loss
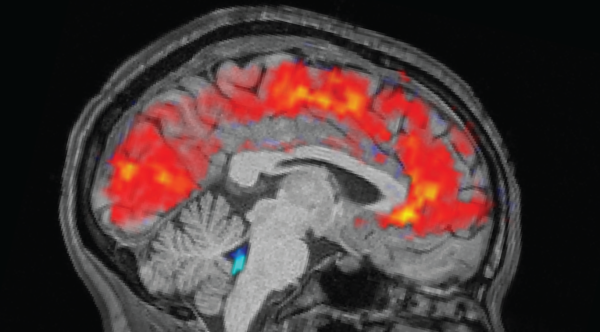
Study reveals why the brain ‘zones out’ when you’re exhausted
‘Chemo brain’ may stem from damage to the brain’s drainage system
Latest in Immune System
