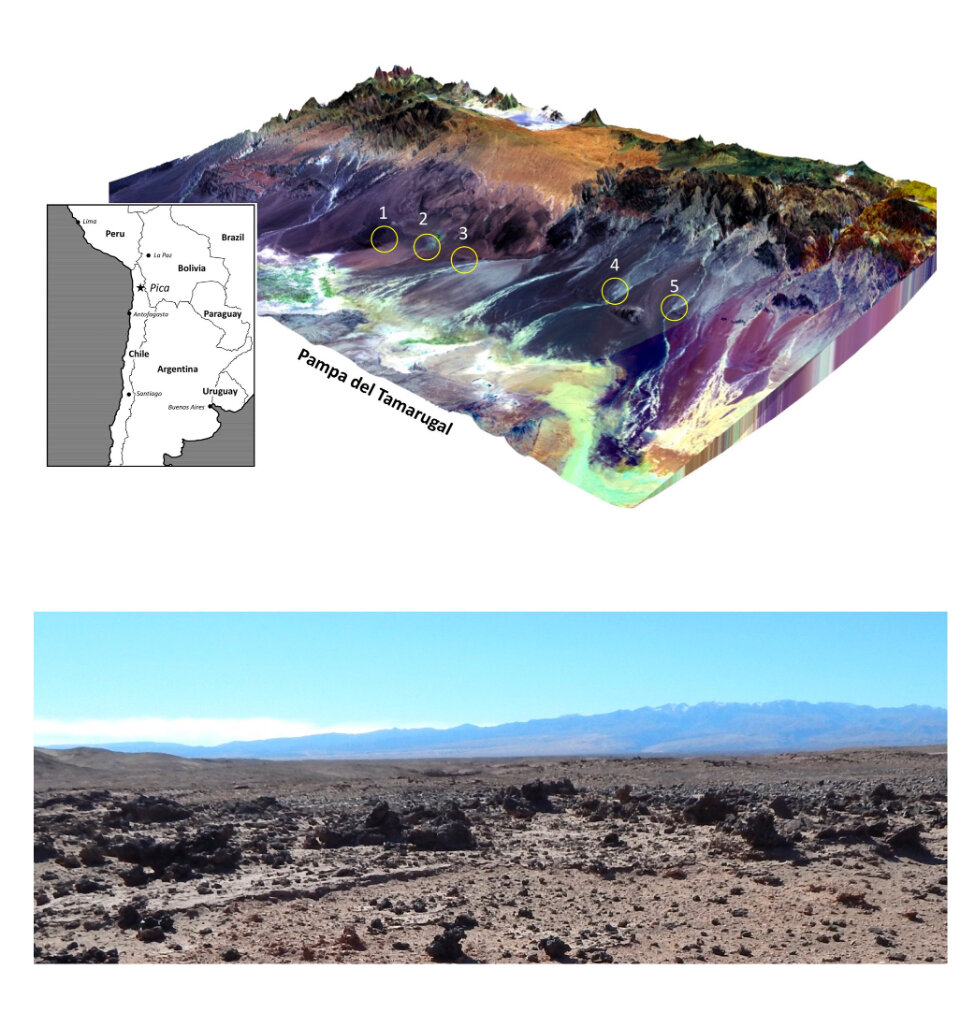
A comet exploded over the Atacama Desert in Chilie. This is the conclusion reached by geologists from the USA. The catastrophe led to the fact that in some places in the desert melted the sand and formed glassy rock.
The work is published in the journal Geology. Residents of the settlement of Pica in the Atacama Desert in Chile have long found pieces of glass with a diameter up to 50 centimeters of dark green and black, scattered along a strip length of about 75 kilometers. Scientists from the Department of Earth Sciences, Brown University (USA) and Santa Tomas University (Chile) have studied these samples and analyzed their distribution on the ground. As a result, they found within the silicates tiny fragments of minerals characteristic of meteorites and other objects of extraterrestrial origin.
Was there really an Atacama comet
In addition, it turned out that these fragments are similar in composition to the minerals of comet 81P / Vilda, delivered to Earth by the Stardust mission in 2004. The researchers concluded that the particles of minerals in the silicate glass, and probably are the remnants of a comet similar in composition to 81P / Vilda. According to them, about 12 thousand years ago, the “uninvited guest” exploded over the Atacama Desert, and its fragments scattered in the sand, melting it and forming a glass mineral.
Evidence that the comet exploded over the Atacama Desert
“This is the first time we have seen reliable evidence that glass on our planet was created by heat radiation and red-hot air currents from a bolide that exploded directly over the Earth. To have such a strong impact on such a large area, it must have been a really powerful explosion, not to be compared with ordinary meteor explosions,” said Professor Pete Schultz of Brown University.
Why have scientists have not put forward a less exotic version of the origin of glass, because it could have been formed, for example, as a result of volcanic activity? First of all, because minerals of extraterrestrial origin were found in the glass. And also because at least some of these pieces of glass, judging by their structure, were formed during a large-scale catastrophe, as they are twisted and crumpled.
This suggests that the fragments were thrown over a large distance. Therefore the version of a forest fire is also excluded (Atacama desert has not always been lifeless – once there were rivers flowing and vegetation was thriving). Zircon minerals found in the glass, partially transformed into baddeleyite – a simple zirconium oxide.
This is possible at temperatures above 1600 degrees Celsius, which, again, rules out any fire. The timing of the explosion of the comet coincides with the period of disappearance of large mammals from this area. However, for the final conclusions about the exact date of the cataclysm and the causal relationship between the extinction of animals and the explosion need further research.