There is no cure for coronavirus – only coronavirus antibodies may help. Not everyone has them. You can teach your body to make them on its own, with a vaccine. Or you can just make them and inject into the patient. The first Russian antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 have already been created and are undergoing pre-clinical tests.
Coronavirus antibodies are already developed
The first Russian development of neutralizing antibodies to SARS-CoV-2, created at the Institute of Molecular and Cellular Biology of the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences, has received a grant from the Ministry of Education and Science for preclinical testing in the amount of 270 million rubles. The details of their research were published in the journal Cell Discovery on the website of the scientific Nature.
Covid-19 antibodies are already being used in treatment
The first phase of preclinical trials and obtaining two antibody producers will be completed at the end of 2022, and the saving antibodies to the virus, which has been killing millions of people around the world for almost two years, should be created within three years. During this time, of course, many changes may occur: on the one hand, the virus will have new strains, and on the other, more people will be vaccinated, which, in turn, will not only prevent the spread of Covid-19 and increase mortality, but also the formation of mutant variants of the causative agent itself.
But one thing will not change for sure: Covid-19 is not going anywhere; we must learn to fight it and keep a close eye on how it mutates and what new dangers it prepares.
The very idea of treating people with coronavirus antibodies is not an innovation. Injection of highly purified blood plasma from overexposed patients for some infectious diseases was practiced in the twentieth century, and today this method is used in some clinics for those infected with the coronavirus. However, antibodies with protective or neutralizing properties represent only a small part of the total pool of antiviral antibodies produced by the immune system. The concentration of neutralizing antibodies in the plasma of cured patients is insufficient for full protection against SARS-CoV-2.
Who needs treatment for coronavirus
Theoretically, antibodies should be produced by the human body itself when encountering the virus, but this process does not always happen in time and in the right amount. Vaccinated people produce their own neutralizing antibodies much faster and in greater quantities than those who have not been vaccinated. But there are quite a few groups of people for whom the vaccine is either contraindicated or it does not provide sufficient antibody titers for protection in any particular case (for example, immunodeficient patients).
Small Antibodies of Big Animals
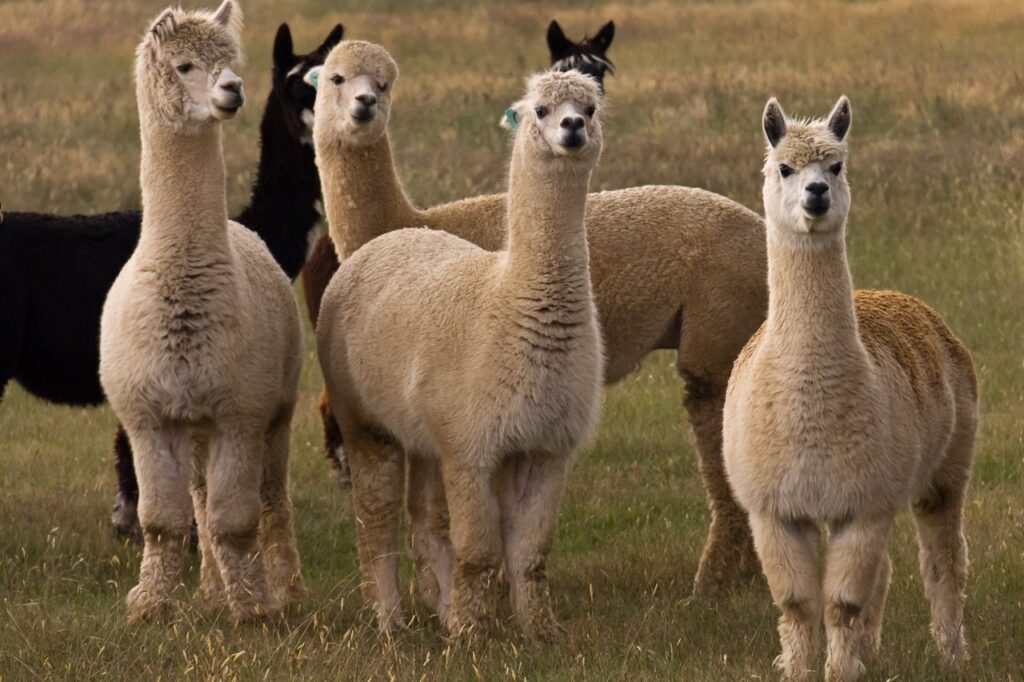

A separate promising direction in the creation of antiviral agents based on monoclonal neutralizing antibodies is the use of antibodies of camels, llamas and alpacas. Camelids can produce antibodies that consist only of heavy chains of immunoglobulins (human antibodies consist of two heavy chains and two light chains). The antigen-binding sites (domains) of these heavy chains are called single-domain antibodies or nanoantibodies, because they are about 10 times smaller than human antibodies – they are six to 10 nanometers in size.
Race to the top
When a new drug is created that should become, if not a cure-all, then at least a means to save a huge number of people, the efforts of many scientific groups around the world are needed. The more of them, the better the chances of solving the problem. Of the three antibody drugs approved for use in the U.S., Sotrovimab, a product of GSK-VIR, has the broadest neutralizing properties. So far, only Sotrovimab has proven insensitive to all known new mutations, including the most aggressive “beta” (South African) variant with very high lethality. Antibody insensitivity to strains is the preservation of the neutralizing function of antibodies, despite the variability of SARS-CoV-2.