The Hyades is a scattered star cluster in the constellation of Taurus. The cluster is 45 parsecs distant and closest to Earth, and has an apparent magnitude of 0.5m. The tidal radius of the Hyades is 9 parsecs, but many stars of the cluster are at large distances from the center of the cluster: in particular, two tidal tails extending to 800 parsecs have been observed. More than 700 stars with a total mass of the order of 435 M⊙ belong to the cluster. The Giads are about 650 million years old, which may indicate a common origin with another cluster, the Manger. During its existence the Giads have lost a significant fraction of their mass and will continue to lose it in the future – the disintegration of the cluster will happen in 30 million years.
The Hyades have been known since antiquity, but are not numbered in the Messier catalog. Many important properties of the Hyades were discovered after the beginning of the 20th century – for example, the tidal tails of the cluster were only discovered in 2018. The cluster is visible to the naked eye and, because of its prominence, is popular with amateur astronomers. The giads played a significant role in ancient Greek mythology and were associated with the rain nymphs, the mythological giads. The cluster was also mentioned in poems from antiquity.
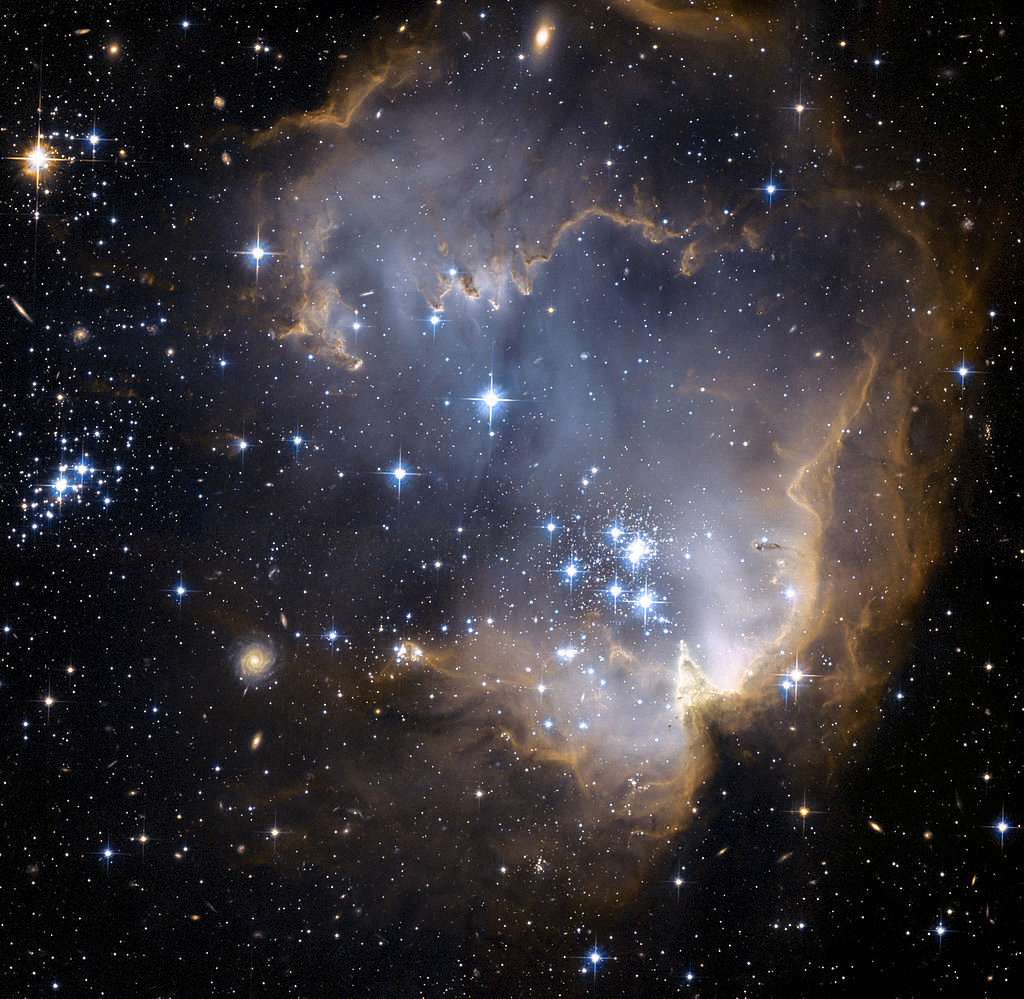
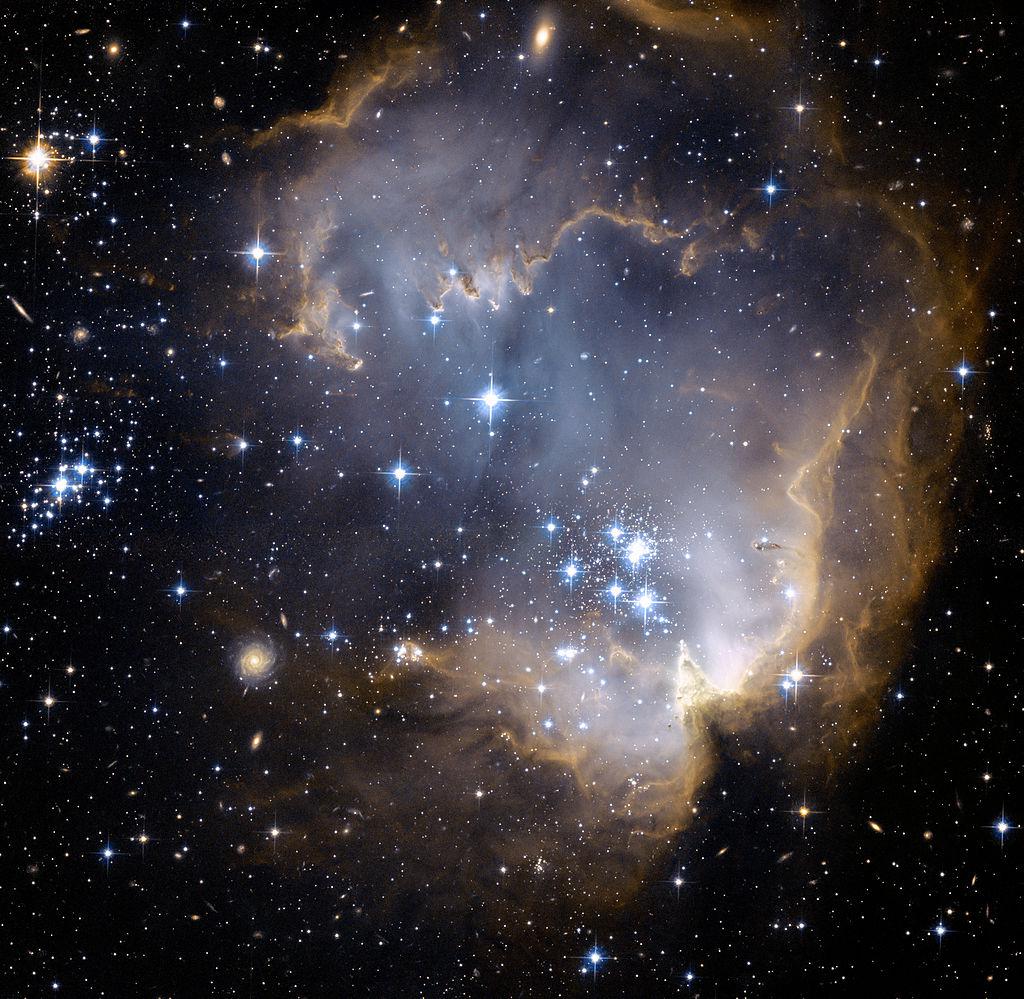
Presented image was obtained by the telescope Hubble. It shows the deep space object known as NGC 602. It is an emission nebula with a diffuse cluster located in the Small Magellanic Cloud.
The diameter of NGC 602 is about 200 light years. Astronomers estimate that the cluster is about 5 million years old. At the center of NGC 602 can be seen a group of particularly bright young stars. Their powerful radiation affects the surrounding gas-dust clouds, forming in them cavities and various bizarre structures.
In addition to NGC 602, numerous background galaxies can also be seen in the Hubble image. They are located much further away from the nebula. The distance to these objects is measured in hundreds of millions or even billions of light years.





