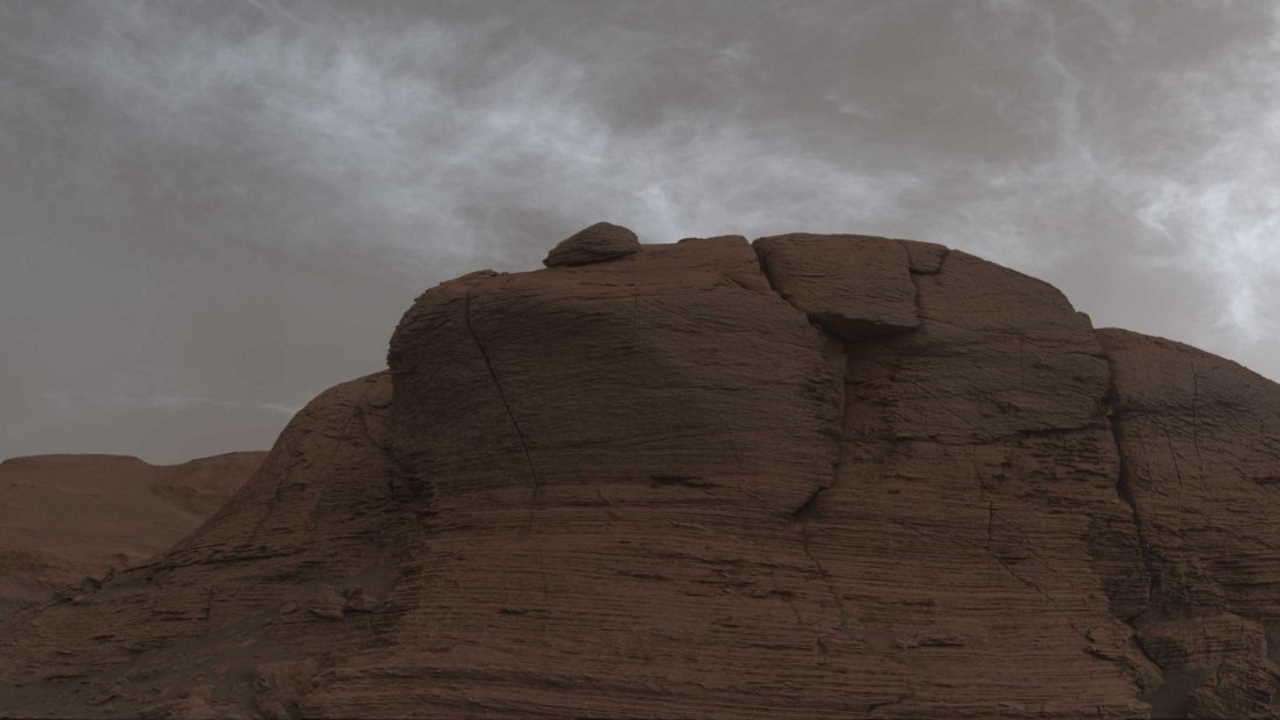
The K’urriosity Mars Rover detected a double-skulled and nacreous twilight after the Sun went down. Typically, the twilight on Mars occur later, at the coldest part of the year. Moreover, they were formed higher and, most likely, contain frozen carbon dioxide.
What is known about storms on Mars?
Gloom in the molten and dry atmosphere of Mars is a rare phenomenon. Typically they occur at the planet’s equator during the coldest part of the year, when the distance between Mars and the Sun is the greatest. Most of them are formed at a height of less than 60 kilometers and are composed of water ice. But one full Martian year ago (or two terrestrial years) investigators discovered that the K’urriosity rover, located in Ґeil Crater, was forming clouds earlier than expected. This year, the team prepared for the fixation of these “early” chmars from the time of their first appearance in late September.
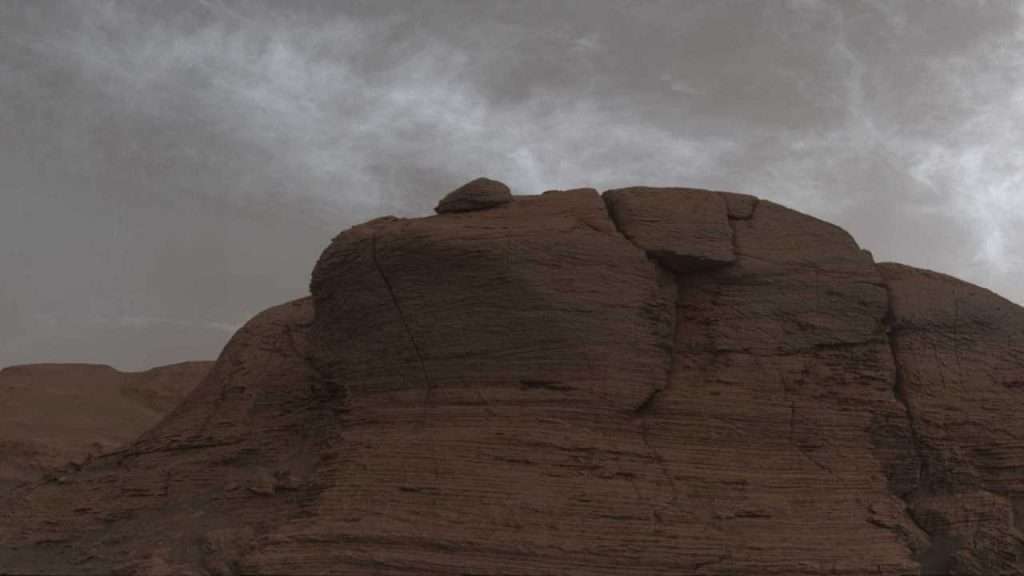

What kind of clouds did the rover detect?
The rover detected several types of chimaeras. Exquisite, delicate twisted structures are easier to see in the black and white images, but the colors can be seen in the Mastcam images. The twilight clouds were bright immediately after the setting of the Sun, because their crystals mirror the light, so they look bright on the dark sky. When the Sun’s position in the sky decreases, these clouds become darker. In addition, the rover also saw shimmering nacreous twilight, particles of which have more or less the same size. Such specks form and grow at the same speed.
Thanks to the rover’s monitoring it was found that “early” clouds form at a higher altitude than usual. Most likely, they are formed from frozen carbon dioxide or dry ice. However, additional analysis is necessary to determine the exact height of the chimeras and to distinguish which of them contain water ice and which contain dry ice.